
Secondly, governments that recruit computer specialists to digitally spy on other governments might influence state decisions and infringe on rights of sovereignty. Firstly, illicit trade deals could be monitored and regulated, strengthening international law enforcement and human rights protections. Retrieving data from these parts of the Web has implications for international relations and law. Drug and gun sales, child pornography, human trafficking, and hitman hires are some of the activities that are conducted within the Dark Web realm. Nevertheless, the nature of the Dark Web easily lends itself to malign purposes. The concept of the Dark Web can thus be traced back to concerns for privacy. For example, journalists that are concerned about their safety in authoritarian regimes have an interest in keeping their work hidden from their government. Initially, the US government helped fund the creation of Tor for circumstances that demand anonymity. Dark Web or Darknet sites comprise of about 1% of all data.
Deep web iceberg software#
For instance, The Onion Router (Tor) is a software that directs Internet traffic or communications through several layers of encryption so that it becomes near impossible to trace content back to the IP address of the user. It can only be accessed through certain browsers.

The Dark Web, on the other hand, is the portion of the Internet that is intentionally hidden from public viewership. According to certain media sources, most notably PJ media, much ‘hacking’ was not required to obtain Clinton documents because there is a relatively low level of security in the Deep Web. Hillary Clinton’s email leaks involved interaction with the Deep Web. A popular analogy given to describe the visible part of the Web is the tip of the larger iceberg. The Deep Web is believed to hold approximately 95% of all the data in the world. For instance, an individual’s gmail account is considered to be part of the Deep Web as it cannot be accessed through a Google search. The Deep Web has also been called the invisible web: data stored on the Deep Web does not appear on conventional search engine queries. Digital Hidden Figures Hillary Clinton, 5/2016, New York Post Cover email (Image by Mike Mozart, via Flickr)

Such virtual activity has profound implications on the future of politics. Thus, the Internet is increasingly becoming a tool to gain leverage over large international institutions and states through government hacking and inter-state espionage. With a rudimentary understanding of the Deep and Dark Web, it is easy to see how cybercrime can go unchallenged and even unnoticed.
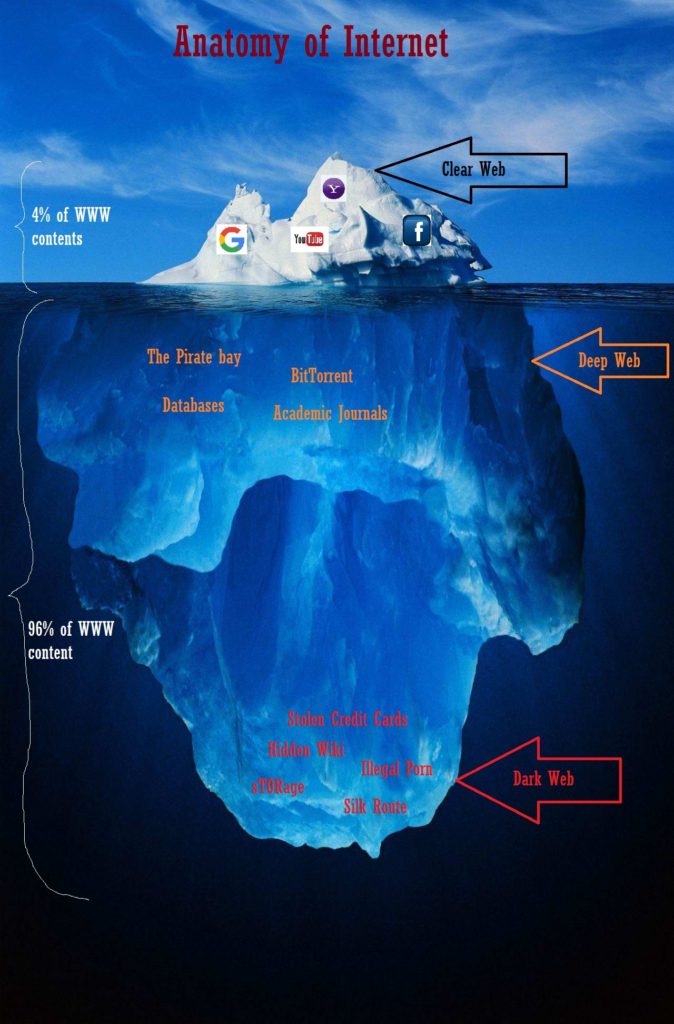
However, it has also been a double edged sword. The Internet has thus proven strong enough to change the dynamics of international politics. State decisions are made upon heaps of intelligence, usually circulating around the Web. Nowadays, diplomacy is conducted through emails and online political forums. Since the advent of the Internet, it has been impossible to prevent the effects of vastly expanded, quickly available information from seeping into the political sphere.

The birth of the World Wide Web in 1989 marked an unprecedented expansion of information and communication, with a remarkable risk – reward ratio. It dominates the lives and practices of many.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
